GREGoR’s main goal is to develop new technologies, genome sequencing strategies and analytical approaches that will aid researchers to identify the cause of rare, unsolved cases with a suspected genetic cause. While the Consortium does not provide clinical advice, its 5 Research Centers (RCs) conduct research studies and work with patients and families affected by rare diseases. These collaborations have resulted in both successful diagnoses and cases that remain unresolved. See How does research participation work? for more information about what to expect when considering participation in a research study, and the Collaboration webpage for information about the studies each RC is conducting and how to contact the GREGoR RCs directly.
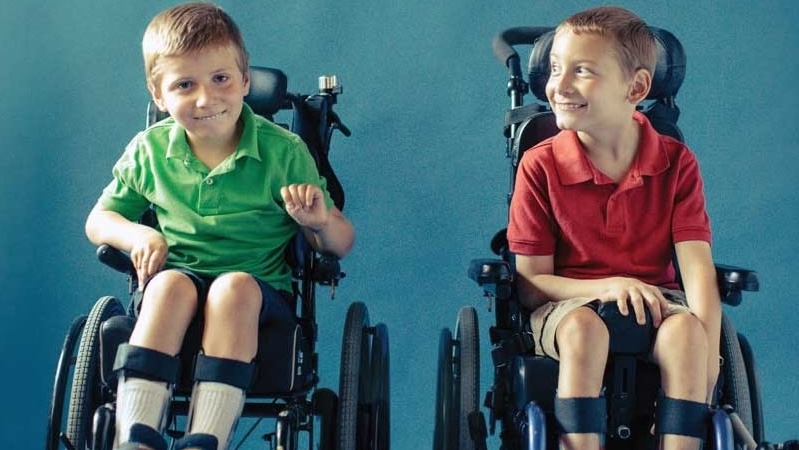

'When you don't know, you feel alone in the world'
GREGoR Stanford Site
Four parents of children with rare diseases share their perspectives on navigating the diagnostic odyssey. Some research participants found out their diagnosis. Others are still waiting.

Emma's match: How connecting patients with ultra-rare disorders can uncover the roots of disease
Broad Institute
For the parents of a young girl with an undiagnosed condition, scientific collaboration among multiple groups of scientists and close connection with the family led to her diagnosis and the discovery of a new genetic disease.
Patients with rare disease meet their matches
Broad Institute
Understanding whether identified genetic variants are disease-related is challenging. A tool called MatchMaker Exchange helps rare disease researchers make scientific connections that can lead to diagnoses for families, like Cameron’s diagnosis of PI4KA-related disorder.

Next-generation genomics testing holds key to undiagnosed rare disease
University of California, Irvine - GREGoR
Researchers from the UCI-GREGoR team encountered a challenging case of an 11-year-old boy who had trouble walking. Despite extensive testing, no diagnosis was found until researchers identified a rare genetic disorder. Fortunately, this genetic disorder was treatable and the boy’s condition quickly improved.
One gene provides diagnoses for 30 patients whose condition was unexplained for years
Baylor College of Medicine - GREGoR
Through an international collaboration between the Baylor College Medicine - GREGoR team and other researchers, a gene involved in metabolite transport was found to cause a broad spectrum of neurodevelopmental disorders including intellectual disability, cerebral palsy, and birth defects
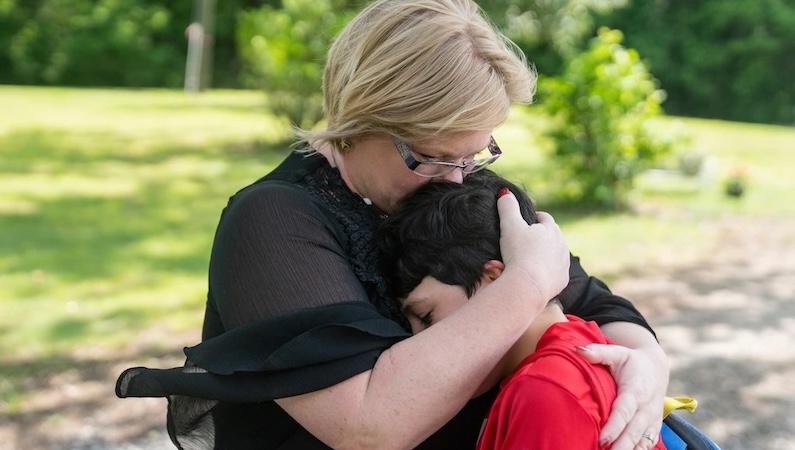

A new, more diverse human genome offers hope for rare genetic diseases
University of California, Irvine - GREGoR
Over twenty years ago the first human genome was decoded, which helped solve many medical mysteries but often provided no treatments. Recently, a new and more detailed version of the human genome, called the pangenome, was created. As science continues to evolve this advancement brings hope for an improved understanding of rare diseases and potentially transforming medical care.
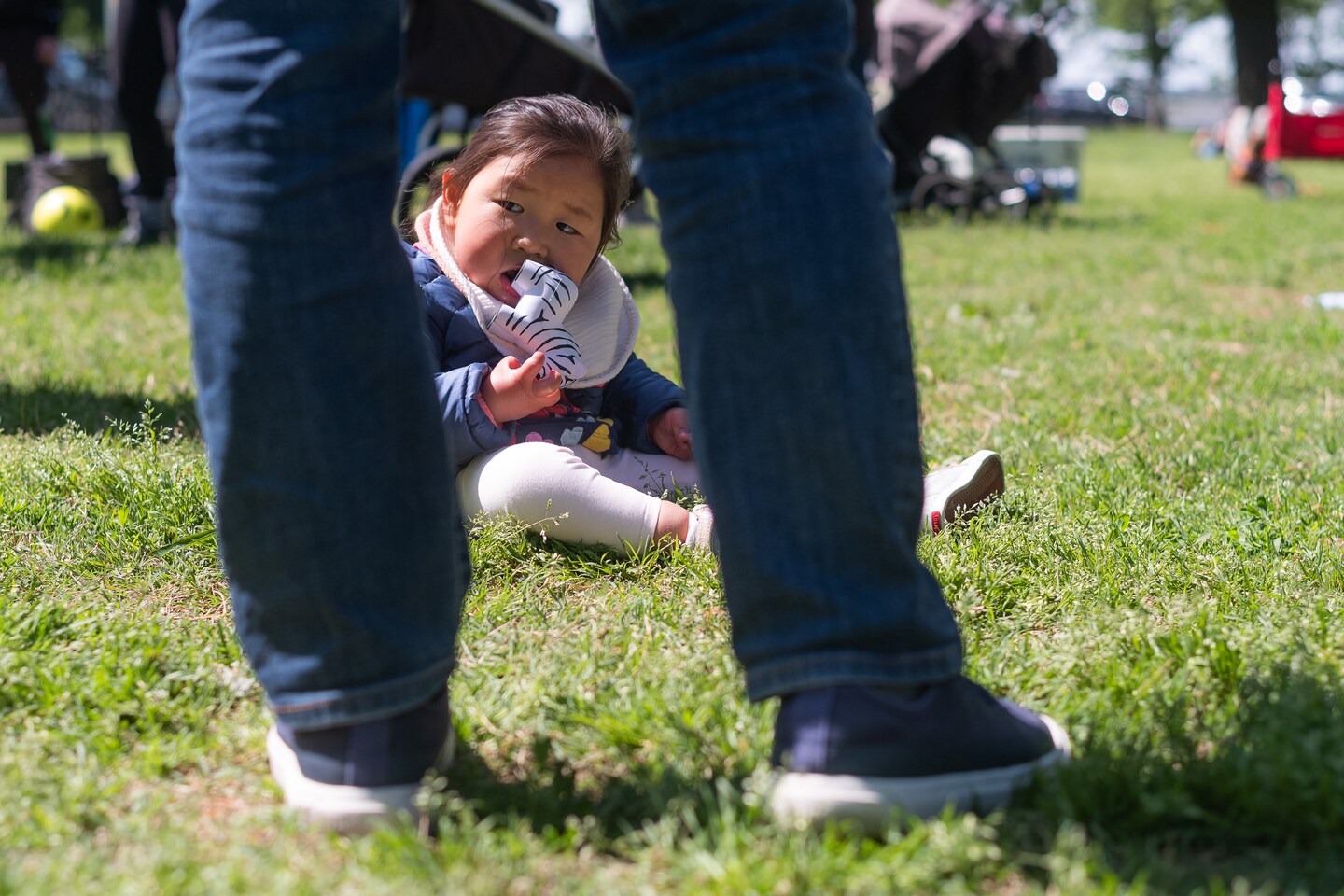

Their children have a rare condition. They didn’t know its name – until now.
Broad Institute & University of California, Irvine - GREGoR
Five families with children who have the newly discovered rare condition, ReNU syndrome, recently gathered in a D.C. park. Scientists believe 100,000 more people have it.
